Methodology
We support you in ensuring the safe and long-term operation of crystalline materials. Structure and phase analyses can, for example, explain the performance of functional ceramics, make the sintering behavior of structural ceramics assessable and enable an evaluation of phase changes in steel materials, such as those that can occur in high-temperature applications, during deformation and due to corrosion.
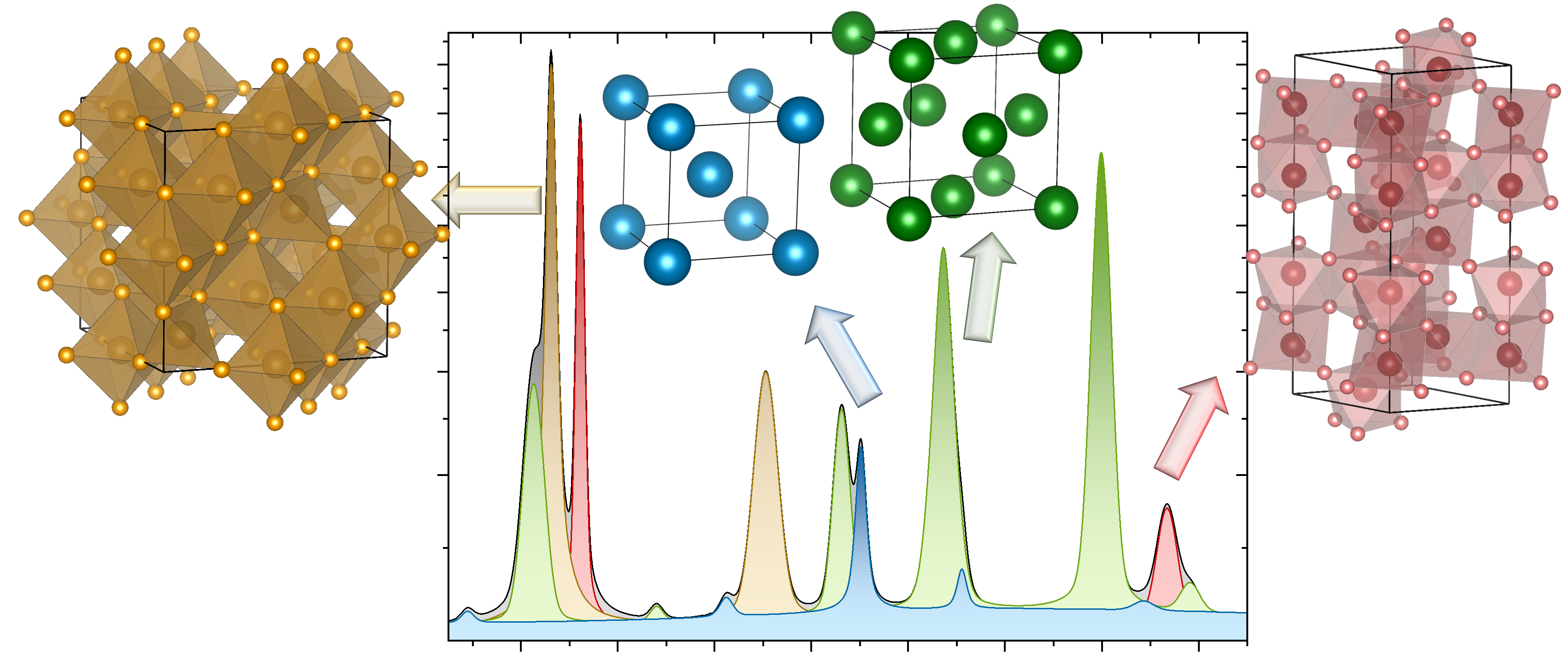
The crystal structure and its phase composition play an important role for technical components and workpieces. This can influence mechanical, electrical, magnetic and other properties. Structure and phase analysis offers the possibility of correlating these properties with the crystals and microstructure, thus explaining changes in properties. X-ray, synchrotron or neutron radiation is used to generate diffractograms that provide information about the atomic arrangement in a polycrystalline component. In the laboratory, conditions can also be generated as they occur in real-world operation of the material or component. These in situ or operando experiments can be conducted with a specified temperature, electric field, magnetic field, mechanical load and many other external stimuli. This makes it possible, for example, to explain the effects of fluctuating process and operating conditions regarding structure and properties as well as to understand the mechanisms of functionality in order to improve the properties of materials and components.
Depending on the measurement method, different sample sizes and penetration depths can be measured. With laboratory X-ray equipment, only a few micrometers (1 - 100 µm) of the surface are usually accessible. Mappings of the structural analysis can be made by scanning the samples. Mobile X-ray devices can be used for on-site investigations. Synchrotron radiation usually generates higher energy levels and is therefore suitable for providing information from the inside of the material in transmission geometry. In addition, complex sample environments for in situ experiments are possible here. Neutron radiation can also be used to measure large samples or components in transition in order to obtain this information. Neutrons are also sensitive to the magnetic structure.
 Fraunhofer Institute for Mechanics of Materials IWM
Fraunhofer Institute for Mechanics of Materials IWM